
/copy-command-options-windows-10-5b7d6ba9c9e77c0050c60eda.png)
- #COMMAND LINE FOR MAC DIRECTORY MAC OS#
- #COMMAND LINE FOR MAC DIRECTORY FULL#
- #COMMAND LINE FOR MAC DIRECTORY PASSWORD#
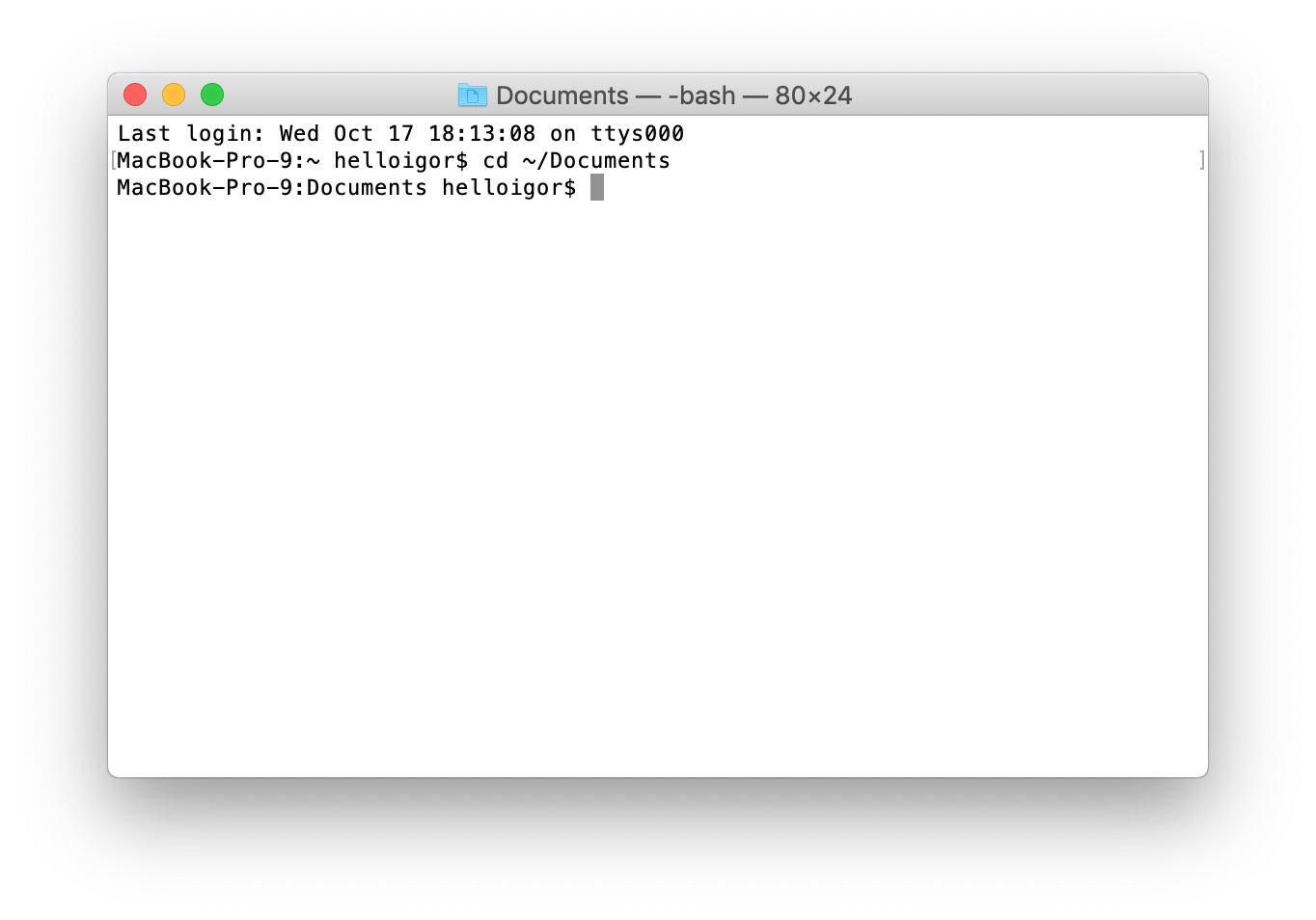
If the working directory was /Users/MyName/Documents, it would change to /Users/MyName. There are some specific shortcuts you can use with the cd command that are summarized below. It's worth noting at this point that all commands are case-sensitive, so cd Documents is not the same as cd documents, and cd is not the same as CD. The prompt changes to MacBook:Documents Jon$. To change to a different working directory use the cd command like so: The working directory is the directory the shell will perform all commands in unless specifically told otherwise. This stands for Print Working Directory and on my machine outputs the path /Users/Jon.
#COMMAND LINE FOR MAC DIRECTORY FULL#
To view the full path of the current directory, type: The ~ indicates that the current directory is my user directory. MacBook is the name of my machine, Jon is my username. Last login: Mon Jan 5 15:27:17 on ttys000 It doesn't matter if yours has a different value to mine.ĭirectory navigationYou will see something like this on screen: If you resize the window these numbers will change. Incidentally, if your title bar doesn't say "bash", type bash and press enter.Ĩ0x24 refers to the number of characters that can be displayed on screen at once - 80 horizontally and 24 vertically. There are various different shells available, each with minor differences. The title bar of my window says "Terminal - bash - 80x24".īash refers to the shell I am using. I find it useful to ctrl-click the dock icon and select Keep in Dock so it is always there for convenience, but this is up to you. Setting upFirst of all, open up the Terminal by navigating to /Applications/Utilities and double-clicking the Terminal application.
#COMMAND LINE FOR MAC DIRECTORY MAC OS#
While most VFX houses use some form of Linux, Mac OS X's Terminal is almost identical with the exception of a small number of proprietary commands. If you are thinking of entering the visual effects industry, most employers will expect basic command-line knowledge and shell scripting abilities. And you don't even need to constantly type things either - you can write a shell script to perform a task and set it to run automatically. You can perform operations on a large number of files at once in a fraction of a second, saving a lot of time.Īlthough the GUI is prettier and more intuitive, constantly moving, clicking and dragging the mouse around the screen wastes time - not to mention that rendering the GUI takes away precious processing cycles from the operation you are trying to perform.

It's really not that scary - in fact, it can actually be a very useful timesaving device. By default, the process will display all processes by CPU usage, with the process id or PID displayed alongside each entry.Getting to know the Terminal Part 1: Basic File OperationsThe Terminal is an application that drives fear into the heart of a lot of Mac users - an application they only dream of using in their worst possible nightmares. To see a list of currently running processes and how much CPU and memory they’re currently using, execute top. This is especially useful for printing a path that you can later copy and paste. To display the current directory that you’re in (or “print working directory”), you can use the pwd command. If you want to edit a system file, for example, you might need to use sudo nano in order to save your changes. Some commands require root access in order to work.
#COMMAND LINE FOR MAC DIRECTORY PASSWORD#
Once you’ve entered a command prefixed by sudo, you’ll be required to enter your administrator password to execute it.

The sudo prefix is used to execute a command as a “super user,” also known as root or admin. To save a file, hit Control+O (known as “Write Out”) or quit without saving using Control+X. Once you’re in nano, pay attention to the commands at the bottom of the screen, which involve the control key. Use cp to initiate the copy command, add a flag where required, and then enter the target file or folder, followed by a space, and then add the destination folder. Remember, you can also use the same location shortcuts that you’d use with the cd command (e.g. For example, use -C to get a multi-column output, -S to sort by size, -lt to sort by date modified, -la for detailed contents including hidden files, or -lh to create a list with readable file sizes. You can add flags to the ls command to get different results. Append it with a location on the drive to specifically target that directory. List Files & Folders: lsĪlso useful in navigating your drive, ls can be used to list the contents of the current directory simply by executing the command. For example, running cd ~ will take you to the Home directory for the current user. You can also use cd/ to get to the root of the drive, cd. You can use shortcuts to quickly skip to certain directories.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
